Life expectancy is a statistical measure of the average number of years a person is expected to live based on factors such as age, gender, and mortality rates. It is commonly used by actuaries, insurance companies, and governments to estimate future population growth, health care needs, and retirement planning. Life expectancy can vary widely between countries, socioeconomic groups, and time periods due to differences in lifestyle, genetics, medical advances, and other factors. It is an important indicator of population health and can influence public policies and resource allocation. Various factors can influence a person's life expectancy. These factors include genetics, lifestyle choices, access to healthcare, socio-economic status, and environmental conditions. By understanding these factors, insurers can better assess the risk of providing coverage to individuals and determine appropriate premiums. Life expectancy plays a crucial role in the life insurance industry. Insurers rely on life expectancy data to evaluate the risk associated with providing coverage to an individual, which in turn influences the cost of premiums and the policy's terms and conditions. Over the years, life expectancy has shown significant improvement globally, leading to changes in the insurance industry. These trends have influenced premium calculations, product offerings, and the industry's overall growth. Life expectancy has generally increased worldwide over the past century due to advancements in medical care, public health initiatives, and improved living conditions. This increase in life expectancy has led to adjustments in the way insurance companies assess risk and calculate premiums. Life expectancy varies by region, influenced by factors such as healthcare access, socio-economic conditions, and lifestyle choices. These regional differences are essential for insurers to consider when assessing risk and determining premium rates for policyholders. As life expectancy has increased, the insurance industry has had to adapt to the changing needs of policyholders. This has resulted in the development of new products and innovative ways of underwriting and risk assessment. Life expectancy is a key consideration for insurance providers when determining premium rates. Insurers use mortality tables, individual factors, and other data to calculate the cost of coverage for policyholders. During the underwriting process, insurance providers assess an individual's risk factors to determine their eligibility for coverage and premium rates. Life expectancy is a significant factor in this process, as it helps insurers estimate the likelihood of a policyholder's death during the policy term. Mortality tables provide essential data on the likelihood of death for different age groups, genders, and other demographic factors. Insurers use these tables, along with other information, to calculate life expectancy and determine appropriate premium rates for policyholders. Individual factors such as health status, lifestyle choices, and occupation can affect a person's life expectancy. Insurers may adjust premium rates based on these factors to accurately reflect the risk associated with providing coverage to a particular policyholder. Life expectancy is an essential factor to consider when choosing the right life insurance policy. Different types of policies and coverage options are available to meet the diverse needs of policyholders. Term life policies provide coverage for a specified period, typically 10, 20, or 30 years. These policies are generally more affordable and can be an appropriate choice for individuals with shorter life expectancies or those who only require coverage for a specific period. Permanent life policies, such as whole life and universal life, offer coverage for the policyholder's entire life. These policies often include a cash value component, which can be an attractive option for individuals with longer life expectancies who want a long-term financial planning tool in addition to insurance coverage. Riders and additional benefits can be added to life insurance policies to enhance coverage and customize a policy to meet the unique needs of the policyholder. Some riders, such as long-term care or critical illness coverage, may be more appealing to individuals with specific life expectancy concerns or health risks. Adopting healthy lifestyle habits, seeking regular medical care, and managing risk factors can improve life expectancy and potentially reduce life insurance premiums. Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol consumption can positively impact life expectancy. These healthy habits can lead to lower insurance premiums, as they reduce the risk factors associated with premature death. Staying up-to-date with medical check-ups and screenings can help detect and manage health issues early, which can improve life expectancy. Regular medical care can also help policyholders qualify for more favorable life insurance rates. Managing and reducing risks related to occupation, hobbies, and lifestyle choices can positively affect life expectancy and insurance premiums. By minimizing exposure to hazardous activities and maintaining a safe living environment, individuals can lower their risk profile and potentially qualify for more affordable coverage. The continued increase in life expectancy has significant implications for the insurance industry, leading to product innovation, changing policyholder needs, and regulatory and ethical considerations. As life expectancies increase, insurance companies must innovate and evolve their product offerings to meet the changing needs of policyholders. This may include developing new types of coverage, expanding policy features, and offering more flexible options for policyholders. Longer life expectancies mean that policyholders may require coverage for an extended period, which can influence their choice of policy type and coverage options. Insurance companies must adapt to these changing needs to remain competitive in the market. As life expectancy continues to rise, regulators and industry professionals must address various ethical and regulatory challenges. It includes ensuring fair pricing, maintaining the solvency of insurance companies, and addressing potential discrimination based on factors that affect life expectancy. Life expectancy significantly influences the life insurance industry, affecting premium calculations, policy selection, and industry trends. Factors such as age, gender, location, and lifestyle choices contribute to life expectancy, which insurers consider during the underwriting process. As life expectancies continue to increase, insurance companies must adapt their products and services to meet evolving policyholder needs. By understanding the role of life expectancy in life insurance and adopting strategies to improve life expectancy, individuals can make informed decisions about their coverage and potentially secure more affordable premiums.Definition of Life Expectancy
Factors Affecting Life Expectancy
Relevance to Life Insurance
Historical Trends in Life Expectancy
Global Changes Over Time
Regional Differences
Impact on Insurance Industry
Role of Life Expectancy in Premium Calculations
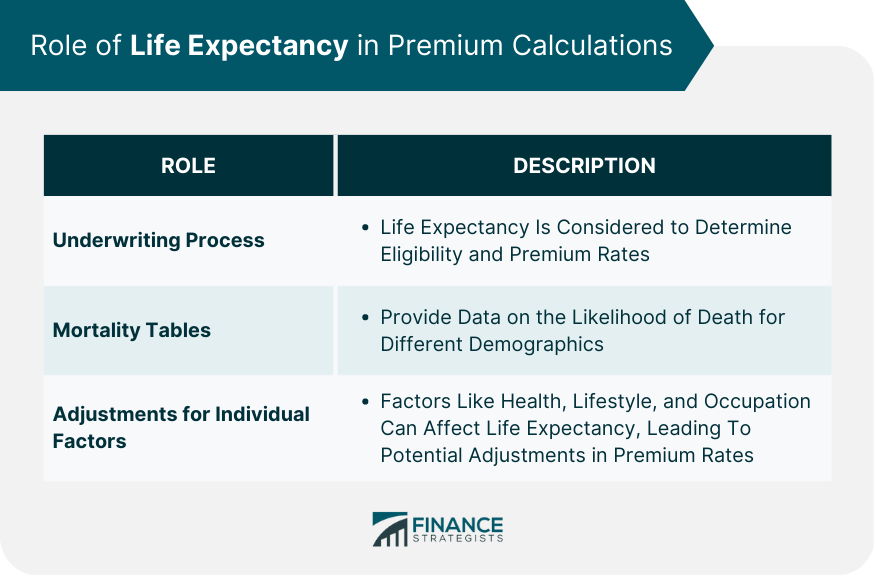
Underwriting Process
Mortality Tables and Their Use
Adjustments for Individual Factors
Life Expectancy as a Consideration in Policy Selection
Term Life Policies
Permanent Life Policies
Riders and Additional Benefits
Strategies for Improving Life Expectancy and Reducing Premiums
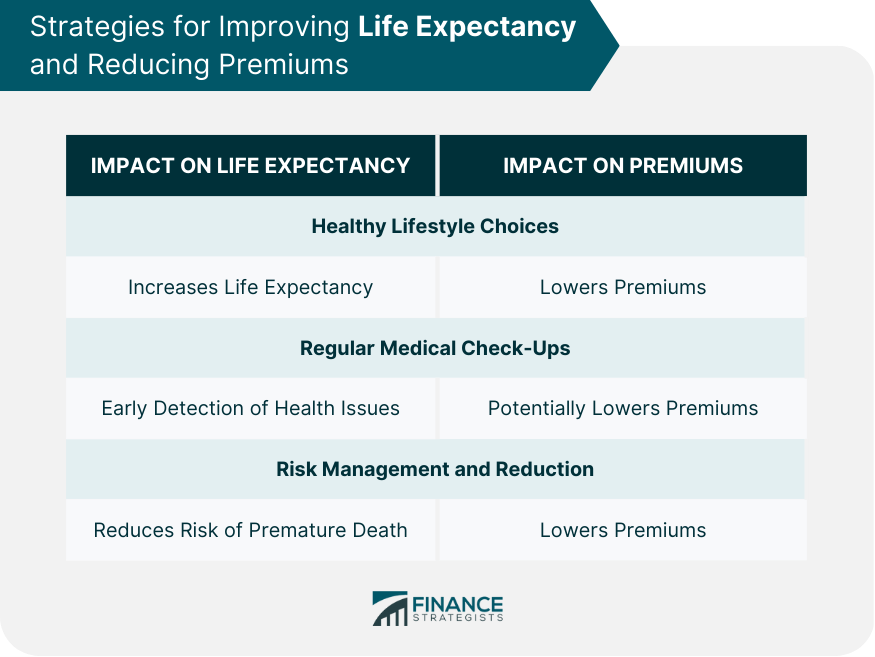
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
Regular Medical Check-Ups
Risk Management and Reduction
Implications of Increasing Life Expectancy on the Insurance Industry
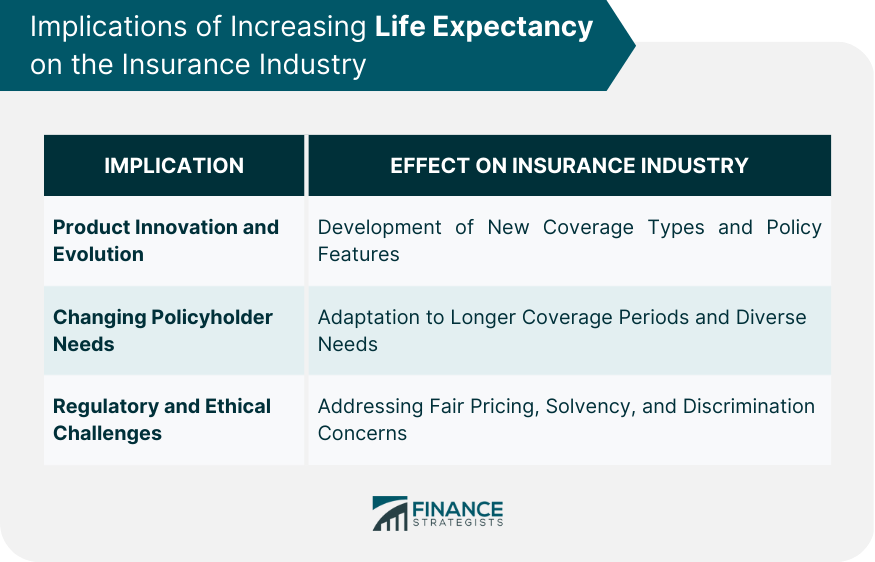
Product Innovation and Evolution
Changing Policyholder Needs
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
Conclusion
Life Expectancy FAQs
Life expectancy plays a crucial role in determining life insurance premiums. Insurers use life expectancy data, along with other factors, to assess the risk associated with providing coverage to an individual. Longer life expectancies generally result in lower premiums, as the likelihood of the insurer having to pay out benefits during the policy term is reduced.
Insurance providers consider several factors that influence life expectancy during the underwriting process. These factors include age, gender, geographic location, health status, lifestyle choices, occupation, and participation in risky activities.
The increase in life expectancy has led to significant changes in the life insurance industry, such as product innovation and evolution, shifting policyholder needs, and addressing regulatory and ethical considerations. Insurers must adapt to these changes to remain competitive in the market.
Yes, improving life expectancy through healthy lifestyle choices, regular medical check-ups, and risk management can help reduce life insurance premiums. By minimizing risk factors associated with premature death, individuals can lower their risk profile and potentially qualify for more affordable coverage.
Insurers use life expectancy data in conjunction with mortality tables and individual factors to calculate premium rates for policyholders. Mortality tables provide essential information on the likelihood of death for different age groups, genders, and other demographic factors, helping insurers estimate the risk associated with providing coverage to a particular individual.
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide, a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University, where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon, Nasdaq and Forbes.